It Happened on
May 03, 1915
280 days later…

born on February 08, 1916 (d. 1973)
Betty Fields
American film and stage actress
born on November 30, 1872 (d. 1918)
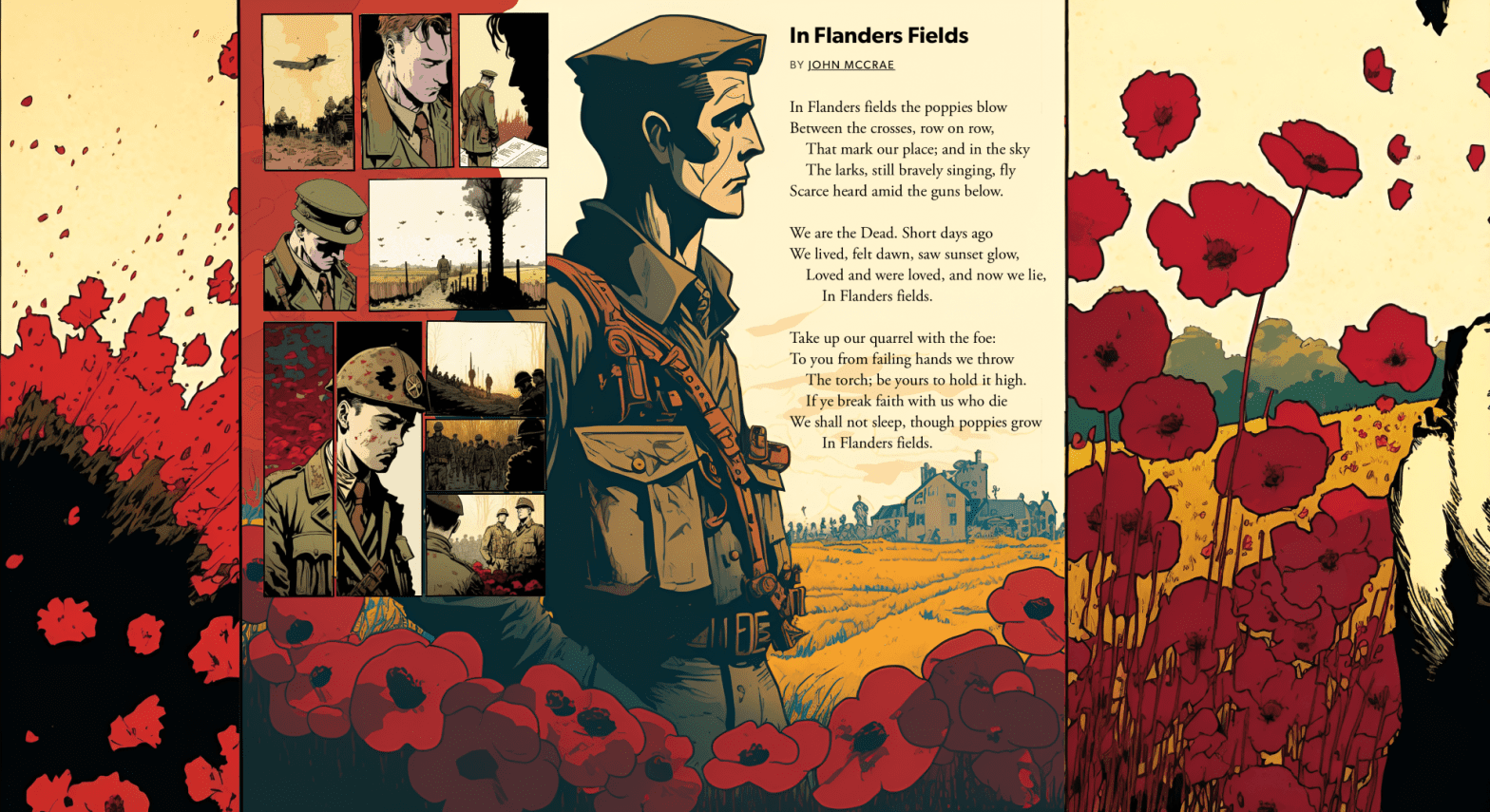
John McCrae
Canadian poet, physician, author, artist and soldier during World War I, and a surgeon during the Second Battle of Ypres, in BelgiumPeople featured in this post:

John McCrae
Canadian poet, physician, author, artist and soldier during World War I, and a surgeon during the Second Battle of Ypres, in Belgium